
My problem is that my old pharmacist used to give me the correct hypodermic’s & now every time I ask the different pharmacists on duty at CVS which size hypo do I need? they never seem to know, & invariably I end up with the incorrect size, either too small for the viscous medicine, or to short for IM.
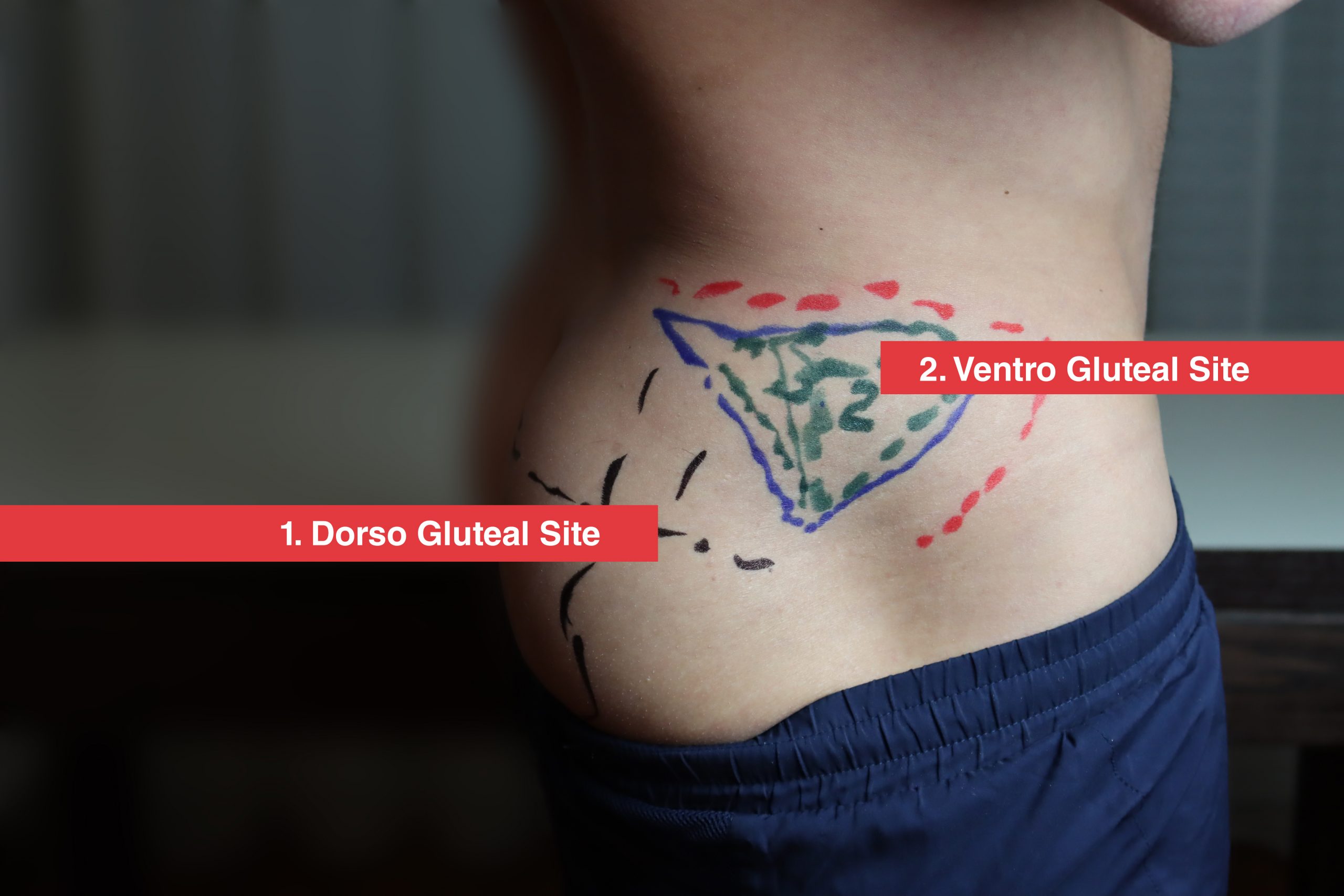
I am a patient who has to take depo-estradiol injections every month. The patient should be positioned so the target muscle is as relaxed as possible. The Z-Track method should be used for IM medication delivery. Whenever possible the VG site should be the preferred location for intramuscular injections.
#Ventrogluteal injection site skin
Inject (slowly) with needle at 90 degrees to skin surface.Apply gentle traction on the skin to pull it away from the injection site (about 2-3 cm).This both reduces pain, and prevents dispersion of medication into subcutaneous tissue. When delivering medications via any IM route the technique of Z-tracking should be used. Inject medication slowly (around 10 seconds per ml), remove needle quickly, and gently apply pressure to site for 10 seconds.There is no evidence for the need to aspirate the plunger when using the VG site.Take care as you are inserting needle in proximity to your fingers. Use your peace sign to spread skin taut.Wipe site with alco-wipe in a circular motion and allow to dry.The injection site is in the middle of this peace-sign.The middle finger then slides across to make a peace-sign pointing up to the iliac crest.First, place the heel of your hand (use your L hand if injecting into the patients R VG and vice-versa) over the patients greater trochanter, and feel for the anterior superior iliac spine with your index finger.One method to locate the correct site is: The ventrogluteal site is located halfway between the hip and the head of the femur. The VG site is also sparse of any major innervating nerves or blood vessels whilst remaining well perfused from smaller branches. The ventorgluteal (VG) site has less subcutaneous fat and a thicker muscle mass than the dorsogluteal site with an almost certain probability of penetrating muscle with a standard needle. Dorsogluteal site has a decreased absorption rate increasing the possibility of a depot effect with drug build up and potential for overdose.Pain receptors are located in the subcutaneous layer, not in muscle tissues and so medication delivered into this area may be more painful.With the increasing incidence of obesity amongst our patients we are probably going to be delivering subcutaneous injections if we choose this location.
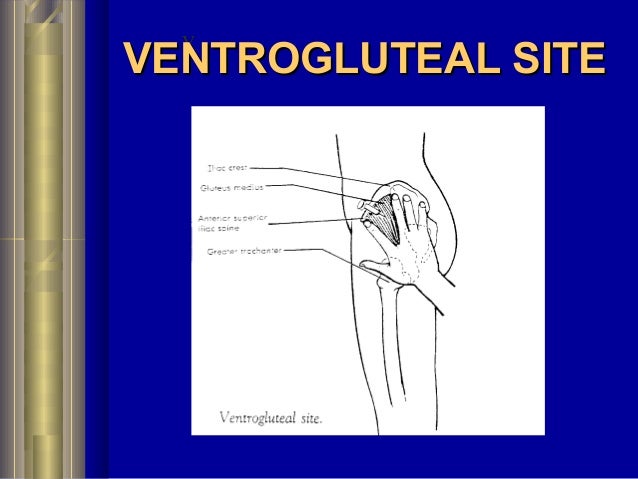
In fact, one study found the success rate of IM injections to be 32% (which fell to 8% in female patients)! A number of studies have found that the depth of muscle in the dorsogluteal region is often greater then the length of a standard needle used for IM injections, resulting in a failure to achieve intramuscular deposition of the medication. It has been taught that you will probably avoid this by further dividing the upper outer quadrant into another quadrant and giving the injection into the upper outer of the upper outer.ĭespite this, there have been reports of injuries to the sciatic nerve leading to problems ranging from foot drop to paralysis of the lower limb.

This is usually done by drawing an imaginary cross (bisecting it vertically and horizontally). It is located by dividing the buttock into four equal quadrants. It is found in the area of the superior lateral aspect of the gluteal muscles, commonly known as the upper outer quadrant. This site been used by nurses for years as the target of choice for IM injections. And I still see many (older) nurses who are continuing to administer intramuscular injections this way.Īs complications from IM injections include abscess, cellulites, tissue necrosis, granuloma, muscle fibrosis, contractures, haematoma, injury to blood vessels, bones and peripheral nerves, it is important we follow best practice guidelines when delivering medications via this route. This is were I had been sticking my needles for many years now, and I have given thousands (if not millions) of injections this way.īut I was wrong.
#Ventrogluteal injection site how to
Some time ago a new-graduate nurse taught me how to give an intramuscular injection.Īfter studiously watching one of our senior staff give an intramuscular (IM) injection, the new-grad informed us that, in fact, she was not taught to give injections into the upper-outer quadrant.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
